Fluid systems
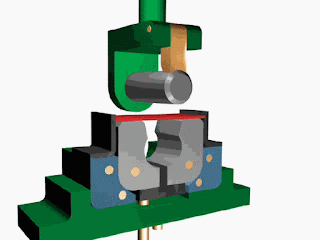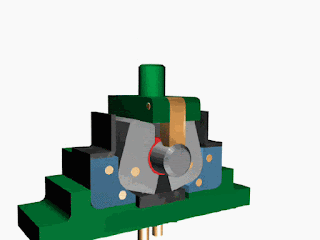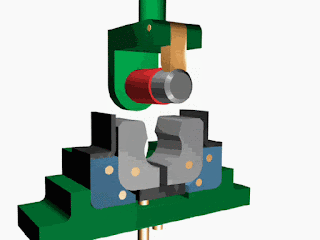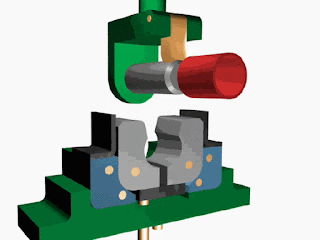
Fluid systems In the industry, the transmission of power from one point to another is carried out using three methods: Mechanical transmission: Mechanical transmission of power is carried through shafts, gears, chains, belts, etc. (As seen in chapter 1) Electrical transmission: Electrical transmission of power is carried through wires, transformers, etc. Fluid power: Fluid transmission of power is carried through liquids or gas in a confined space. Fluid power is the technology that deals with the generation, control, and transmission of forces and movement of mechanical elements or systems with the use of pressurized fluids (both liquid and gases) in a confined system. The fluid power system includes a hydraulic system ( hydra meaning water in Greek) and a pneumatic system ( pneuma meaning the air in Greek). Hydraulic fluid power systems employ pressurized liquid petroleum oils and synthetic oils, whereas pne...