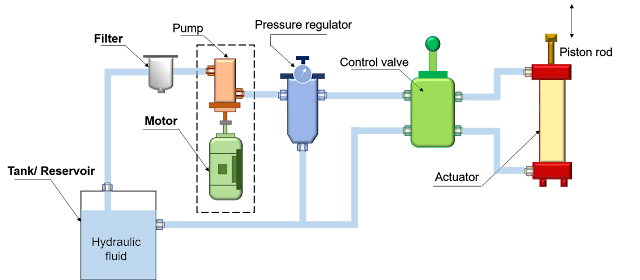
Hydraulic Pressure Relief Valve

The need for Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) A pressure relief valve (PRV) is one of the most important types of safety valves. These types of valves set a limit on the rise of pressure within a hydraulic line or system. In normal operation, the valve is closed and no fluid passes through the PRV. But if the pressure in the line exceeds the limit, the valve opens to relieve the pressure. This protects the expensive machines such as pumps, motors, and actuators from getting damaged due to extensive pressures. Without a relief valve, pressure can continue to grow until another component fails and pressure is released. The need for Pressure Relief Valve (PRV) Types of Pressure Relief Valve Direct Acting PRV Pilot Operated PRV Direct Acting Pressure Relief Valve Direct-acting PRV is held closed by the direct force of a mechanical spring. The spring force holding the valve closed is opposed by the system hydraulic pressure. The cracking pressure is the pre