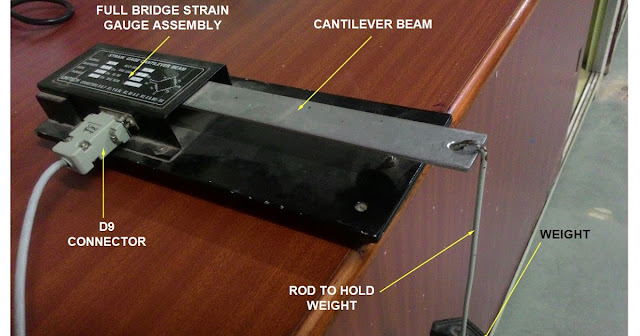
What is a force? In science, force is the push or pull on an object with mass that causes it to change velocity (to accelerate). Force is represented as a vector, which means it has both magnitude and direction. According to Newtons 2nd law of motion F = m·a Where F = force, m = mass, and a = acceleration Force measurement The most popular method for measuring force is using a strain gauge. We measure the strain developed due to force using strain gauges; and by multiplying the strain with the effective cross-sectional area and Young’s modulus of the material, we can obtain force. Load cells and Proving rings are two common methods for force measurement using strain gauges. We will first discuss the principle of strain gauge and then go for the force measuring techniques. Let us now understand what is the strain? What is the strain? The strain is the amount of deformation of a body due to an applied force. More specifically, strain (e) is defined as the fractional change in ...