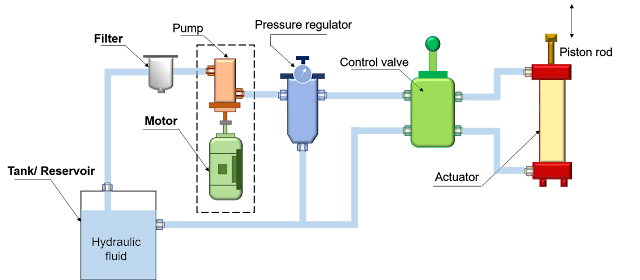
Key elements of a typical hydraulic system
- Tank/ Reservoir: The reservoir holds the hydraulic fluid (liquid petroleum oils and synthetic oils, usually oil) required for the hydraulic system.
- Filter: Filters are used to remove any foreign particles so as keep the fluid system clean and efficient, as well as avoid damage to the actuator and valves.
- Motor-driven Pump: The hydraulic pump is used to force the fluid from the reservoir to the rest of the hydraulic circuit by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. The hydraulic pump which is the heart of the hydraulic system converts the mechanical energy int hydraulic energy. The mechanical energy is delivered to the pump via a prime mover such as an electric motor.
- Pressure regulator: The pressure regulator, as the name implies, maintains the pressure level of the hydraulic fluid. Whenever excess pressure level is generated, excess fluid is doped back into the reservoir.
- Control valves (CV): CVs are used to control the direction, pressure, and flow rate of a fluid flowing through the circuit.
- Actuator: The hydraulic actuator is a device used to convert fluid power into mechanical power to do useful work. The actuator may be of the linear type (e.g., hydraulic cylinder) or rotary type(e.g., hydraulic motor) to provide linear or rotary motion, respectively. The pressurized hydraulic fluid delivered by the hydraulic pump is supplied to the actuators, which converts the energy of the fluid into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is used to get the work done.
- Piping system: The piping system carries the hydraulic fluid from one place to another.
Working of control valve:
OFF state of the control valve
Extend state of the control valve
Retract state of the control valve






Comments
Post a Comment