Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic Systems
- Pneumatic technology deals with the study of behavior and applications of compressed air in our daily life in general and manufacturing automation in particular.
- Systems using compressed air for power transmission are called pneumatic systems. When air is compressed and stored, it can be used as a medium for carrying out mechanical work, measurement, and controlling and operating equipment and machines. Figure 1 shows how an extend and retract system can be implemented using pneumatics.
- Pneumatic systems use air (which is compressed) as the medium which is abundantly available in the atmosphere and can be easily exhausted into the atmosphere after completion of the assigned task.
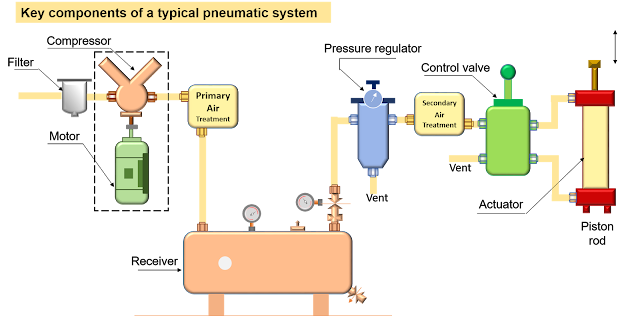
Figure 1. Key components of a typical pneumatic system
A pneumatic system essentially consists of following
- motor-driven compressor,
- air receiver;
- directional control valve (DCV);
- pneumatic cylinder.
Let us see the operation of each component in detail
- Air filters: These are used to filter out the contaminants from the air.
- Compressor: Compressed air is generated by using air compressors. Air compressors are either diesel or electrically operated. Based on the requirement of compressed air, suitable capacity compressors may be used.
- Primary air treatment: A primary air treatment stage may consist of an air cooler and an air dryer.
- Air cooler: During compression operation, air temperature increases. Therefore coolers are used to reduce the temperature of the compressed air.
- Air Dryer: Air humidity and dew point are raised by compression. The excess moisture has to be removed in order to safeguard pneumatic elements. This water vapor or moisture in the air is separated from the air by using a dryer.
- Air Receiver: A pneumatic system uses compressed air, and the air is usually stored in a pressure vessel called an air receiver. Air is delivered to the air receiver by a motor-driven compressor. The compressor is controlled by a pressure switch in order to start/stop the compressor depending upon the demand.
- Secondary air treatment: The secondary air treatment stage may consist of air service equipment that has an air lubricator. Sometimes, air filter and air regulator is also used in the secondary air treatment stage if required.
- Air filter: The task of the filter is to remove any solid contaminants that are present in the air flowing through the filter.
- Air regulator: The air regulator regulates the pressure of air flowing through the pneumatic system.
- Air lubricator: The secondary air treatment provides oil mist to lubricate and also incorporates further filtration of water particles.
- Control Valve (Directional-CV): The movement of the pneumatic actuator is controlled by a DCV which directs the air into various pressure ports and releases the air from the actuator to the atmosphere.






Comments
Post a Comment